|
Hand surgery involves the non-surgical and surgical
treatment of disease, injury and malformations of the hand, wrist and forearm.Depending on the training level and
interest, hand surgery can also include the elbow and upper arm. In addition, certain diseases of the foot and injuries
of the peripheral nervous system are also treated by hand surgeons.
Diseases - injuries of the hand (examples):
(Additional, more extensive explanations under "Clinical Pictures in Hand Surgery" )
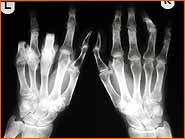
- Arthritis (wear and tear, age-related or gender dependent after injury to joints)
- Heberden's arthritis (distal interphalangeal joints)
- Bouchard's arthritis (proximal interphalangeal joints)
- Rhiz arthritis (carpometacarpal articulation of the thumb)
- Other joints can also be affected, but such cases are rare.
- Chronic polyarthritis (Rheumatoid Arthritis)
- Inflammation disease of the synovial fluid of tendon sheaths, joints and bursa
- Joints and tendon sheaths of the hand are often affected
- Can lead to severe limitation of hand function when left untreated
- Dupuytren's contracture
- Tumor-like, benign disease of the palmar fascia (aponeurosis) which encroaches
upon the fingers and leads to increasing flexion contractions of the finger
- Infection by bacteria or fungus (paronychia, panaris, phlegmon, abscess)
- Malformation of the hand
- Syndactyly (skin and also sometimes bone connection between two, and rarely, more than two fingers)
- Polydactyly (Additional fingers, usually 6 Fingers on one hand)
- Less common severe arrested development malformations resulting in extensive limitation of function or complete loss of function
- Entrapment neuropathy
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (median nerve)
- Loge de Guyon syndrome (ulnar nerve in middle hand area)
- Ulnar tunnel syndrome (ulnar nerve in elbow area)
- Radial tunnel Syndrome (radial nerve of the fore arm)
- Pronator teres syndrome (median nerve of the fore arm)
- Tenosynovitis (tenon sheath inflammation)
- Stenosing tenosynovitis (trigger finger)
- de Quervain's tendovaginitis (Narrowing of the first extensor tendon process in the area of the wrist)
- Inflammation of other tendon sheaths with differing causes
- Tumors
- Benign tumors (very common)
- Ganglion, giant cell tumors, lipoma, enchondroma, hemangioma, epithelial cyst
- Malignant tumors (uncommon)
- Squamous epithelium - carcinoma, all forms of soft tissue and bone sarcoma
- Injuries of the hand
- Sprains and bruises (distorsions)
- Bone breaks (fractures)
- Luxations (dislocations)
- Torn ligament
- Sharp (knife, saw, ...) and blunt (contusion) injuries with damage to tendons, nerves, vasculature, muscle and other soft tissues
 back to top back to top
|
 |
 |