|
The human hand is an extremely sophisticated
organ that can carry out complex functions:
- Movement (motor function): grabbing, holding, supporting
- Sensory functions (sensibility): surface condition (rough, smooth, soft, hart, sharp, dull, cold, warm)
- Gestures: greetings, hints, defensive postures, emotional expressions
The importance of the human hand is made evident through the numerous words and phrases containing the word hand
(Various adages and expressions are given as examples throughout this website).
Anatomically the hand is made up of:
- Bones (27 bones and various small sesamoid bones)
- Joints with capsule-ligament-apparatus (approximately 29 joints
and adjacent small joints between the sesamoid bones and the adjacent bones)
- Muscles
"extrinsic" musculature (located at the fore arm with tendons which attach to the hand and transfer force):
Extensor musculature:
- Extensor for the wrist
- Extensor for the finger
Flexor musculature::
- Flexor for the wrist
- Flexor for the finger
"intrinsic" musculature (located within the hand with local force transfer):
Ball of thumb musculature::
- Constitutes form of ball of thumb
- Mobilizes the thumb over all possible levels and brings it into an opposing position, making a precise grip possible.
Muscles of the ball of the little finger:
- Constitutes form of the ball of the little finger
- Mobilizes the little finger over all possible levels and, much like the thumb, brings it into an opposing position,
for example for the gripping of round objects.
Metacarpal musculature:
- lies between the metacarpal bones
- contributes to the form of the middle hand, usually only apparent in the case of muscle atrophy
- flexes the fingers at the base joints
- extends the fingers at the middle and end joints
- spreads and draws together the fingers
- important for precise movement of the fingers
- Tendons
Muscles transition into tendons. The tendons are situated on specific bone areas and transfer the force to the bones
and joints and in this way enable the movement of joints (extension, flection, abduction, adduction, and rotation).
- Tendon sheaths
Extensor and flexor tendons are at certain points encased in tendon sheaths (synovialis) which lubricate the tendons
and enable them to glide.
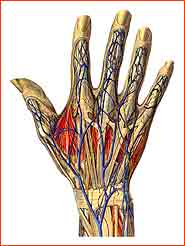
- Vasculature
Arteries (majority situated on the flexor side of the arm and hand)
- Upper arm artery (brachial artery)
- Forearm arteries (radial and ulnar arteries)
- Hand arteries (superficial and deep palmar arterial arch, ulnar metacarpal arteries, collateral digital arteries)
Veins (majority situated on the extensor side of the fore arm and hand, additional smaller veins accompanying arteries)
- veins of the fingers and middle hand
- veins of the fore arm and upper arm(vena basilica u. vena cephalica)
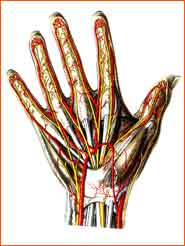
- Nerves (three main nerves for the fore arm and hand)
Median nerve
- Motor function: part of the flexor musculature of the fore arm and hand (extrinsic musculature)
and part of the intrinsic hand musculature
- Sensory function: flexor side of thumb, pointer, middle and ring fingers. Extensor side of the
distal and radial sides of thumb, pointer, middle and ring fingers.
Ulnar nerve
- Motor function: Parts of the flexor muscles of the fore arm and hand (extrinsic musculature)
and a part of the intrinsic musculature
- Sensory function: flexor side of the ulnar side of the ring finger, the little finger, and the extensor side of the
ulnar side of the ring finger and little finger and the middle hand
Radial nerve
- Motor function: hand and extensor muscles of the forearm
- Sensory function: radial side of the middle hand and proximal part of the thumb, pointer finger, and middle finger
- Fat and connective tissue
serves as filling and cushioning material, sometimes also providing form
 back to top back to top
|
 |
 |